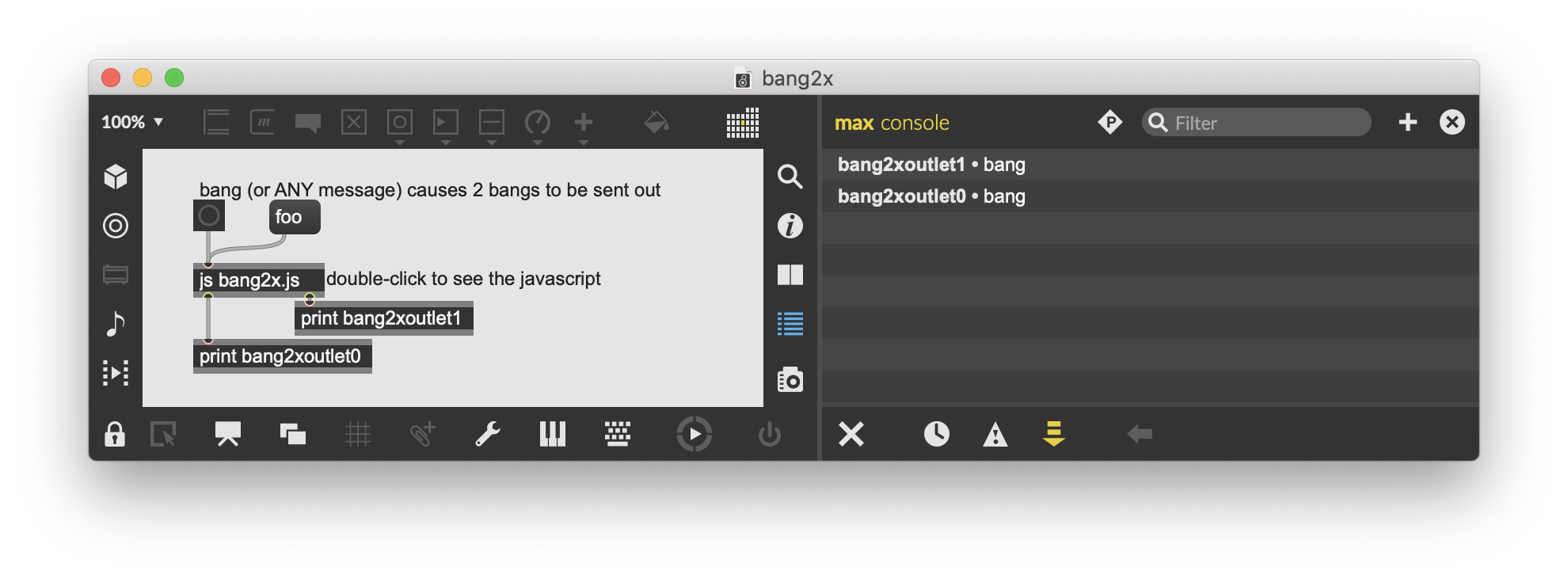
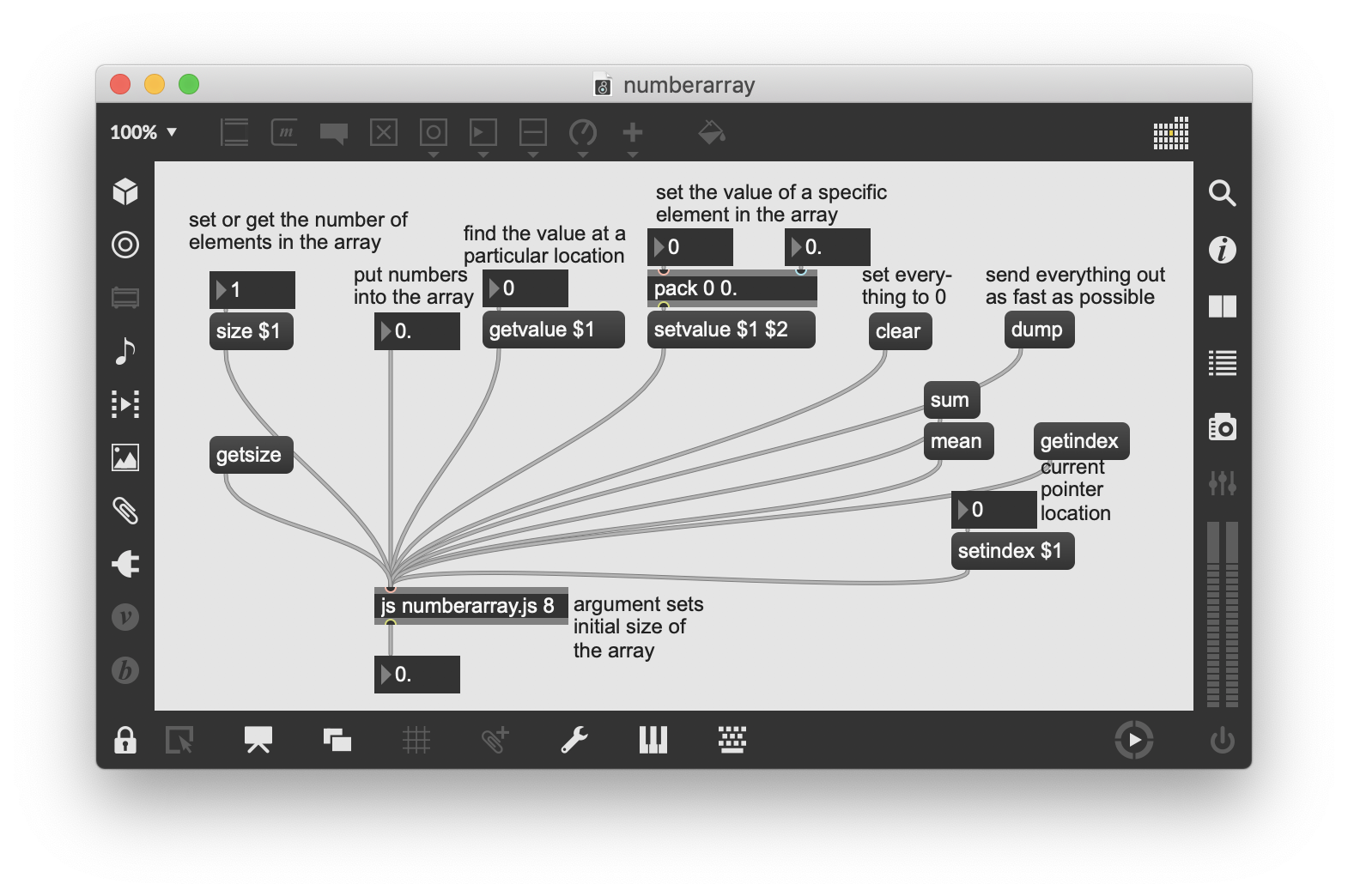
// this is an object that stores the most recently received values in an array
// and allows you to access the array in various ways
// technically you could store strings in an array in addition to numbers, but
// in this object we'll restrict the contents of the array to numbers
// the object will have just one inlet and one outlet
inlets = 1;
outlets = 1;
// this is a declaration of the array where we'll keep the goodies
// declaring an array is different from declaring a single variable
// the default size of thearray will be 1, but the user can change that
// by typing in a size argument or by sending a size message
thearray = new Array(1);
// if there's a typed-in argument in the object box, use that to set the size of the array
if (jsarguments.length > 1) { // if true, that means there's at least one typed-in argument
if ( jsarguments[1] > 0 ) { // check to see that it's a valid argument
thearray.length = parseInt( jsarguments[1] ); // use it to set the length of thearray
} // notice that we parsed it as an integer before using it to set the length of thearray
else { // otherwise,
post( "Error in js", jsarguments[0], ": invalid argument for array size\n");
}
}
// this is a declaration of a global variable
// that will always point to the array index where we'll store the next received number
var i; // i is the name of the index pointer to the location of the next received number
// use that index pointer to step through the array,
// and set all the values in thearray to 0 initially
for ( i = 0; i < thearray.length; i++ ) { // set i to 0, test i after each pass, then increment i and repeat
thearray[i] = 0;
}
i = 0; // set the index pointer to point to the beginning of the array
// we'll start it at the beginning of thearray,
// so the first number will be placed at the beginning of the array
// this gives the user a method for changing the size of thearray
function size( arraylength ) { // the provided number will be in the arraylength argument
if ( arraylength > 0 ) { // check to see that it's a valid argument
thearray.length = parseInt( arraylength ); // use it to set the length of thearray
i = i%thearray.length // in case the size was reduced, make sure i is within thearray.length
}
else { // otherwise,
post( "Error in js", jsarguments[0], ": invalid argument for size\n" );
}
}
// make it possible also to query the object about the size of thearray
function getsize() { // the same function with the word "get" in front of it queries for info
outlet( 0, thearray.length ); // report the size of thearray
}
// when a number comes in, place the incoming number there
// and increment the index (modulo the array length)
function msg_float( incoming ) { // when a float is received
thearray[i] = incoming; // put the incoming number there in the array
i = (i+1)%thearray.length; // increment the index (modulo the array length)
}
// same thing for an integer
function msg_int( incoming ) { // when an int is received
thearray[i] = incoming; // put the incoming number there in the array
i = (i+1)%thearray.length; // increment the index (modulo the array length)
}
// to get a single stored value out of the array
function getvalue( theindex ) {
if ( (theindex >= 0) && (theindex < thearray.length) ) { // make sure it's a valid index
outlet( 0, thearray[theindex] ); // if so, send out the value stored there
}
else { // otherwise, post an error message
post( "Error in js", jsarguments[0], ": invalid argument to getvalue\n" );
}
}
// to set the value at a particular location in the array (without regard to the current index i)
function setvalue( theindex, thevalue ) {
if ( (theindex >= 0) && (theindex < thearray.length) ) { // make sure it's a valid index
thearray[theindex] = parseFloat( thevalue ); // if so, store thevalue there (0 if it isNaN)
}
else { // otherwise, post an error message
post( "Error in js", jsarguments[0], ": invalid array location to setvalue\n" );
}
}
// to get the current location of the index pointer i of the array
function getindex() {
outlet( 0, i );
}
// to set the location of the index pointer i
function setindex( theindex ) {
if ( (theindex >= 0) && (theindex < thearray.length) ) { // make sure it's a valid index
i = theindex; // if so, set i to that location
}
else { // otherwise, post an error message
post( "Error in js", jsarguments[0], ": invalid array location to setindex\n" );
}
}
// to set all values in the array to 0
function clear() { // step through the whole array, setting the values to 0
var j; // local variable for use within this function
for ( j = 0; j < thearray.length; j++ ) { // set it to 0, test it after each pass, then increment and repeat
thearray[j] = 0;
}
}
// to output all values in the array as fast as possible
function dump() { // step through the whole array, sending out the values
for ( j = 0; j < thearray.length; j++ ) {
outlet( 0, thearray[j] );
}
}
// to output all values in the array as a list
// (the receiving object in Max must be able to handle the list length)
function dumplist() { // sending out all the values as a space-separated list
outlet( 0, thearray ); // Max JavaScript support formats the array as a list for you
}
// output the sum of all the elements in the array
function sum() {
var thesum = 0.; // local variable for use within this function
for ( j = 0; j < thearray.length; j++ ) {
thesum = thesum + thearray[j]; // add 'em up
}
outlet( 0, thesum );
}
// output the mean value of all the elements in the array
function mean() {
var thesum = 0.; // local variable for use within this function
for ( j = 0; j < thearray.length; j++ ) {
thesum = thesum + thearray[j]; // add 'em up
}
outlet( 0, ( thesum / thearray.length ) ); // divide thesum by the number of elements
}
// what else would you want to know about the array?
// minimum, maximum, indexOf, lastIndexOf, prev, etc.